Want to make sure your website or app design is effective and usable?
This article compiles 45 design testing methods to help you do just that.
Usability testing, A/B testing, first click testing – each one has its own benefits that can help you gather valuable feedback about how well your design works for your target audience.
But don’t worry – choosing a UX research method doesn’t have to be daunting.
This article will walk you through everything you need to know. (Hopefully it’s bookmark worthy)
Plus, we’ll give you some tips and best practices for conducting successful tests.
The 45 Best Design Testing Methods and Techniques
- A/B testing: A/B testing is a method of comparing two versions of a website or app to determine which one performs better by showing them to a random sample of users and measuring a set of predefined metrics.
- Card sorting: Card sorting is a method of organizing information by grouping related items together based on user’s perception and understanding.
- Click testing: Click testing is a process of evaluating the usability and functionality of a website or application by measuring how real users interact with specific buttons or links.
- First click testing: First click testing is a user testing method of evaluating the user experience by observing where users click on a webpage or application during their initial interaction with the interface.
- Cognitive walkthroughs: A cognitive walkthrough is a usability testing method used to evaluate the effectiveness of a user interface by simulating a user’s thought process and actions.
- Heuristic evaluation: A Heuristic evaluation is a usability evaluation method that involves having a small group of experts examine a user interface and identify any potential usability issues or problems.
- Contextual inquiry: A Contextual inquiry is a qualitative research method used to gather information about how people interact with a specific product, service, or system in their natural environment. It involves observing and interviewing users while they perform tasks.
- Diary studies: A Diary study is a research method that involves individuals keeping a detailed record of their daily experiences, thoughts, and behaviors over a period of time. It is often used in fields such as psychology and sociology to understand patterns and trends in human behavior and emotions.
- Direct observation: Direct observation is a research method in which a UX researcher directly observes and records the behavior and actions of participants in a study. This method can be used in both naturalistic and controlled settings and can provide valuable information on a wide range of topics.
- Ethnographic research: Ethnographic research is a qualitative research method that involves the study of human societies and cultures. It involves observing and interacting with people in their natural environments, and analyzing data through the use of field notes, interviews, and other data collection techniques.
- Eye tracking: Eye tracking is a technology that uses a device to track the movement and position of a person’s eyes. It is commonly used in research and user experience testing to understand visual attention and behavior.
- Five second testing: Five second testing is a method used to evaluate the effectiveness of visual design elements by asking participants to quickly look at a design and recall what they saw within five seconds.
- Focus groups: Focus groups are a research method used to gather information and feedback from a group of individuals on a specific topic or product. They are typically led by a moderator and often involve group discussions and exercises to gather qualitative data.
- Guerrilla testing: Guerrilla testing is a type of user testing that is conducted in an informal and unstructured manner. It is often done in public places and with a small, random sample of participants, in order to gather quick and spontaneous feedback on a product or service.
- Information architecture testing: Information architecture testing is the process of evaluating the organization and structure of a website or application in order to ensure that it is intuitive and easy for users to navigate.
- In-person usability test: In-person moderated usability testing is the most popular UX testing method of evaluating the user experience of a product or website by observing users as they interact with it in a real-life setting.
- Remote usability tests: Remote usability testing is a method of evaluating the usability of a website or application by having users complete tasks and provide feedback while accessing the system remotely, typically through a web-based platform.
- Interviews: Interviews are a method of gathering information by asking questions and obtaining verbal responses from a person or group of people. They can be conducted in various formats, such as face-to-face, over the phone, or via video conferencing.
- Journey mapping: Journey mapping is a process of visualizing and understanding the steps and experiences a customer or user goes through when interacting with a product or service.
- Landing page optimization: Landing page optimization is the process of improving the design and content of a landing page to increase its effectiveness in converting visitors into customers or leads.
- Loading time testing: Loading time testing is a process of measuring the amount of time it takes for a webpage or application to fully load and become usable for the user.
- Long-term field studies: Long-term field studies involve extended observation and research of a particular subject or environment over a period of several months or years.
- Online surveys: Online surveys are a method of collecting data through the internet by asking a set of questions to the participant group.
- Paper prototyping: Paper prototyping is a method of creating a low-fidelity model of a user interface or product design using paper and pencil.
- Personas: Personas is a tool used in user research and user-centered design to create detailed profiles of the people for whom a product or service is being designed.
- Playback testing: Playback testing is a method of evaluating the performance and functionality of a software application by replaying recorded user interactions.
- Scenario testing: Scenario testing is a method of testing software applications that involves creating realistic scenarios that the application may encounter in real-world use, and then testing the application’s behavior and performance under these conditions.
- Accessibility testing: Accessibility testing is the process of evaluating a website or application to ensure that it can be easily used by people with disabilities. This includes testing for things like keyboard navigation, screen reader compatibility, and color contrast, among other things.
- Click-stream analysis: Click-stream analysis is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data about website visitors’ interactions and user behavior on a website. This information can be used to improve the user experience, increase conversion rates, and identify areas of potential revenue growth.
- Concept testing: Concept testing is a research method used to gather feedback on new product or service ideas before they are fully developed. It helps companies determine whether there is a market for their idea and identify potential improvements or changes that need to be made.
- Experience sampling: Experience sampling is a method of research that involves repeatedly collecting data on an individual’s thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in naturalistic settings over a period of time. Usually the participant receives a notification to capture data in the moment.
- Heat maps: Heat maps are a visual representation of data that uses color-coding to display the intensity or density of a particular variable. They are commonly used to analyze website visitor behavior, such as clicks and scroll depth, in order to understand how users interact with a particular page or website.
- Iterative testing: Iterative testing is a method of testing in which the testing process is repeated multiple times in order to identify and fix defects in a software application.
- Longitudinal studies: Longitudinal studies track the same individuals over time in order to understand how a particular variable, such as health or behavior, changes over the course of their lives.
- Card sorting: Card sorting is a method used to help organize and understand information architecture. It involves grouping similar items or topics together using physical cards or digital tools.
- Participatory design: Participatory design is a design process that involves collaboration and active participation from all stakeholders, including users, designers, and decision-makers.
- Pluralistic walkthroughs: A Pluralistic walkthrough is a method for evaluating software design in which a group of experts from different disciplines and perspectives review and provide feedback on the project.
- Rapid prototyping: Rapid prototyping is a method of creating physical models or prototypes of a product or UX design quickly and efficiently.
- Root cause analysis: Root cause analysis is a problem-solving method that aims to identify the underlying cause of a problem or usability issue. It involves identifying symptoms, gathering data, and analyzing the data to determine the root cause, with the goal of implementing a solution that addresses the root cause rather than just the symptoms.
- Tree testing: Tree testing is a method of evaluating the effectiveness and usability of a website’s information architecture. It involves presenting users with a simplified, hierarchical representation of the website’s structure and asking them to find specific pieces of information.
- Wizard of Oz testing: Wizard of Oz testing is a method of testing a product or service by simulating its functionality using human interactions rather than relying on automated systems.

How To Decide Which Method Is Best For You
It’s important to note there is no one-size-fits-all approach for user research and testing designs.
Sometimes a combination of methods is needed to comprehensively understand the usability problem, especially when the design problem is complex.
When researching a design problem, it is important to consider what research method will best align with your goals and data needs.
The number one deciding factor when considering which research method to use, is that the research method aligns with your research questions.
Here are a few more things to consider when deciding which approach to use:
- What are your research goals? Quantitative research is more suitable if you are trying to test hypotheses or establish cause-and-effect relationships. Qualitative research is more suitable if you are trying to gain a deeper understanding of a topic or explore new phenomena.
- What type of data do you need? If you need numerical data or statistics, quantitative research may be the better choice. Qualitative research may be the better choice if you need more in-depth data about people’s attitudes, beliefs, and experiences.
- How much resources do you have? Qualitative research typically requires more time and money than quantitative research.
- What kind of population are you studying? Qualitative research methods tend to work better with smaller samples and allows to get rich data, when quantitative tends to work better with larger samples and can provide generalizability.
All methods have their own advantages and limitations, and the best approach is the one that fit best with the research question, time, budget, and target audience.

The Important Difference Between Qualitative And Quantitative Methods
Qualitative and quantitative research are two different approaches to gathering and analyzing data.
Qualitative research is used to understand underlying reasons, opinions, and motivations. This type of research is often used to explore new or complex phenomena.
Qualitative research is used to understand underlying reasons, opinions, and motivations. Quantitative research collects data that can be quantified.
Quantitative research collects data that can be quantified, such as numerical data, statistics, and metrics. This type of research is often used to test hypotheses, measure variables, and determine cause-and-effect relationships.
Depending on the problem, a mix of methods can also be applied. This would be called mixed-methods research.
Whether to use qualitative or quantitative methods depends on the research goals questions, the type of data needed, and the resources available.
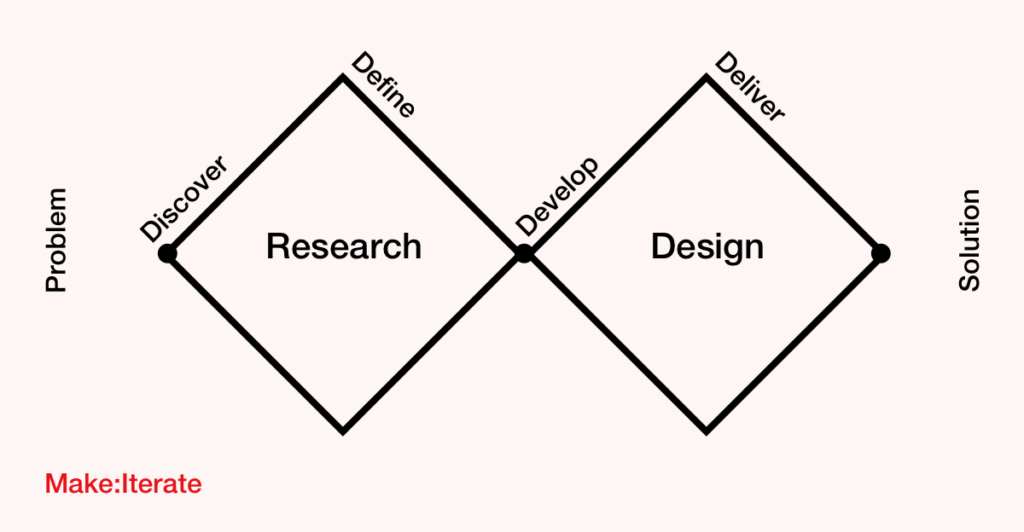
Choose The Best Methods For Each Phase Of Design
Creating and developing a product can be divided into several stages, each with its own focus and objectives.
The Discover Phase
Usually, the process begins with an initial exploration phase, where the main goal is to understand the problem, user needs and identify potential opportunities.
This stage is important to establish the direction and strategy of the product, and the methods used at this stage are often focused on generating ideas and concepts.
The main goal of the initial exploration phase is to understand the problem and user needs.
These can include user research, user interviews, design thinking, and other methods that help to gather information and insights about the problem and users.
The Define Phase
As the product begins to take shape, the design phase begins.
The main focus of this phase is to create and refine a design that addresses the identified needs and goals.
In the design phase, a product’s design is refined and feedback is gathered to improve the design.
Methods used in this stage are formative, providing feedback and information to improve the design.
This stage includes usability testing, first-click tests, concept screening, and other methods that provide insights into the design and user interaction.
The Develop Phase
Once the product is developed and ready for testing, it goes through a final evaluation phase.
The main goal of this phase is to assess website usability and the product’s overall effectiveness and ensure that it meets its intended purpose.
The final evaluation phase of product development is to assess website usability and the product’s overall effectiveness.
This phase can include AB testing, usability testing, surveys, and other methods that measure the product against its goals and objectives and earlier versions or competitors.
It’s important to note that the stages of product development are not always a linear process, and iteration between the stages is common.
Depending on the company, product, and context, the distinction between these stages can vary, but the key is to keep the user at the center of the process and make sure the usability testing methods align with the goals and objectives of the project.
7 Useful Tips And Best Practices For Testing Designs
- Clearly define the goals and objectives of the research. This will help guide the design of the research study and ensure that the findings will be useful and relevant to the product or service being developed.
- Select the right participants. Recruit test participants that are representative of the target user and recruit a mix of participants based on differences in demographic, cultural, and psychographic traits.
- Use a variety of research methods. Combining both quant and qual methods will give you depth and breadth of insight. Experiment by pairing different research methods and combining them to better understand the value each method can provide.
- Be flexible and iterative. Be open to changing the research plan based on the findings, and plan for multiple rounds of testing to gather more data over time. Product design and development is iterative, and so is research. As you learn more and your curiosity develops, you’ll discover the best questions to ask. Adapt your research plan accordingly.
- Observe and listen. Be an active observer and listener during the research and pay attention to the user’s verbal and nonverbal cues. This takes practice to master; it’s a real art. But anyone can begin by simply observing and listening carefully.
- Communicate clearly and share findings with the team. Summarize the key findings from the research, and share them with the relevant stakeholders and the design team, who can use the findings to inform product decisions. Depending on your workplace’s culture, a detailed report followed by a short snappy summary is usually the best approach.
- Follow ethical guidelines. Always be aware of the ethical implications of conducting user research and ensure that all participants are treated respectfully and their privacy is protected. Let participants know what you plan to do with the results and whom you plan to share. Ask them to sign consent forms if you want to reveal their face and identity to your team and stakeholders.
Conclusion
- Design testing is important to ensure your website or app design is effective and usable.
- There are many different design testing methods available, each with its own benefits.
- You can choose the best method for each stage of design, depending on what you want to test.
- Some tips and best practices for conducting successful tests include being clear about the research goals, selecting the right participants, using various research methods, and being flexible and iterative in your approach.
- Guerilla testing is when we take an informal and unstructured approach to testing like asking the public on the street to take part in user tests on the spot.
- Moderated tests take a lot of time and preparation but give the best results for qualitative research. Moderated testing usually requires a larger team to help plan, observe and capture the data.
- Unmoderated testing is useful when you don’t have much time and you need results quickly.
- Each test participant should be chose based on your screening criteria. They should be selected based on how representative they are of your real users.