The DVF framework is a product prioritization method that helps teams to evaluate three key aspects of a successful product: desirability, viability and feasibility.
This article explores how to use IDEO’s DVF framework to create an innovative design solution from idea all the way through final execution and testing, by utilizing the three key elements of desirability, viability, feasibility.
Did you know?
To help teams implement Design Thinking, we offer bespoke innovation training workshops. Talk with us and find out how we can help transform the way you design your products and services.
Interested? Message us in the bottom right corner or learn more here.
What Is IDEO’s Desirability, Viability, Feasibility Framework?
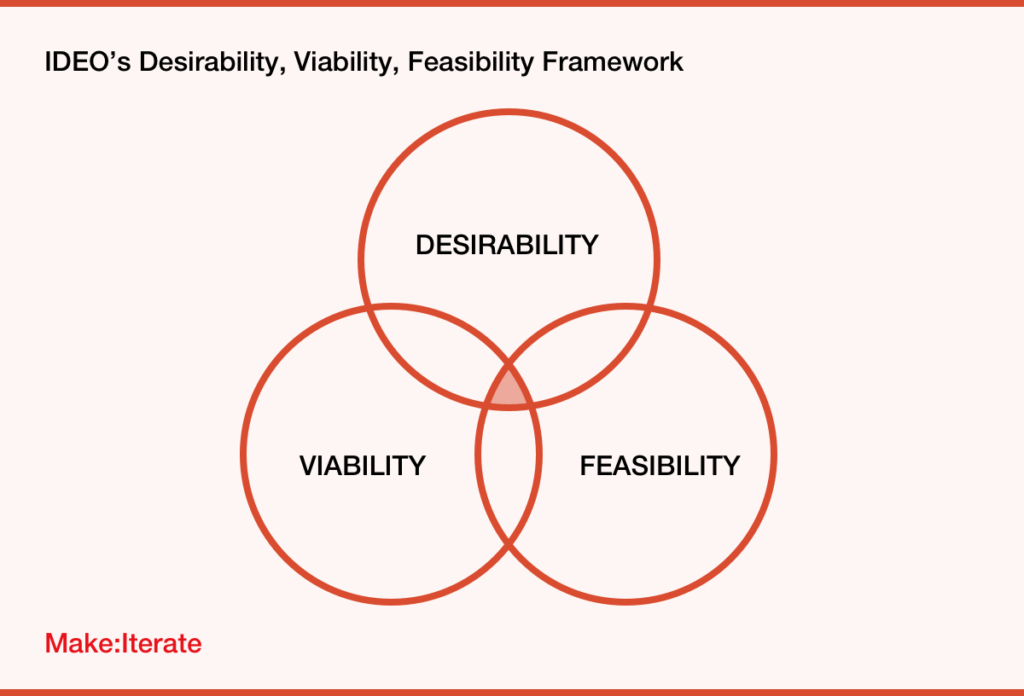
IDEO’s Desirability, Viability and Feasibility (DVF) framework is a powerful tool that helps teams create successful products.
It provides insight into the three key factors necessary for success – whether end-users find it desirable, if it can be created realistically from a technical standpoint and its financial viability.
Through this process you’ll know what product will most likely capture user interest and meet peoples needs, while also being feasible to create with potential long-term sustainability.
The process involves evaluating each of these factors separately, then bringing them together to get a well-rounded view of the likelihood of success for each product or feature.
IDEO’s Desirability, Viability and Feasibility (DVF) framework is a powerful tool that helps teams create successful products by evaluating three key factors separately and bringing them together.
By considering desirability, viability, and feasibility at each stage of the development process, product design teams can reduce uncertainty and create products that are not only technically feasible and financially viable, but also highly desirable to users.
One way to use the DVF framework is to give each idea a rating based on how desirable, viable and feasible they are. Then tally up the total to get a number representing all three criteria. This can help designers prioritize and focus their efforts on the most promising ideas.
The DVF framework is the perfect accompaniment to the design thinking process as it helps us to ensure business success while keeping with a human centered approach.
The Importance of Considering Desirability, Viability, and Feasibility
It’s important to consider all three elements of IDEO’s DVF framework (desirability, viability, and feasibility) in product development because they all play a critical role in the success of a product.
Desirability refers to how much people want the product and whether it meets their needs and desires.
If a product is not desirable to users, it is unlikely to be successful, no matter how technically feasible or financially viable it is.
In order for a product to be successful, it is important to consider all three elements of DVF framework: desirability, viability, and feasibility.
Feasibility refers to whether it is technically possible to create the product. If a product is not feasible to create, it will be difficult or impossible to bring it to market, regardless of how desirable it is to users or how financially viable it is.
Viability refers to whether the product is financially sustainable. If a product is not financially viable, it will not be a sustainable business and will eventually fail, even if it is highly desirable to users and technically feasible to create.
By considering all three elements of the DFV framework, product development teams can create products that are not only technically possible and financially sustainable but also highly desirable to users. This increases the chances of success for the product and the business.
Uses for the DVF Framework
Some specific uses of the DVF framework include:
Evaluating ideas: The DVF framework can be used to evaluate and prioritize ideas during the innovation process. By considering desirability, viability, and feasibility, teams can determine which ideas are most promising and worth pursuing.
Assessing ideas for a minimum viable product (MVP): The DVF framework can be used to assess which features and functionality are most important to include in an MVP. This can help teams create a product that meets users’ needs while being technically feasible and financially viable.
The DVF framework can be used to evaluate and prioritize ideas, assess features for an MVP, and ensure that a product meets customer needs.
Ensuring that a product, service, or value proposition meets customer needs: The DVF framework can be used to ensure that a product, service, business model or value proposition meets the needs and desires of customers. By considering desirability, teams can ensure that the product is something that users will want, while feasibility and viability help ensure that the product can be created and financially sustainable.
7 Benefits of Using the DVF Framework
The DVF framework (desirability, viability, and feasibility) can be a powerful tool for product and service design teams to ensure their products meet customer needs and are successful.
This framework helps teams focus their efforts on the most promising ideas, create an MVP that meets users’ needs, and ensure that the product or service is technically feasible.
1. Ensure an idea meets the needs and wants of the customer
It helps to ensure that a product idea meets the needs and wants of the target customer. To evaluate the desirability of an idea, conduct user research to understand how well the idea aligns with a user’s goals, needs and pain points.
2. Identify any technical or logistical issues
It helps to identify and address any technical or logistical issues that may hinder the development or success of the product. By consulting with technical experts throughout the activity, you can tease out any complicated technical issues that might hinder successful development. Your technical consultants can also help to ideate on alternative possible solutions within the technical constraints.
3. Assess potential market demand and competition
It helps to assess the potential market demand and competition for the product. By considering desirability and gaining evidence to support your decision-making, you’ll also get a good insight into potential market demand and how well your solution compares to competitors.
4. Determine long-term viability of product or service
It helps to determine the long-term viability and scalability of the product. By considering costs of development, maintenance and potential profit that could be generated from the idea. You can assess wether or not it is worth investing in.
5. Prioritize the most promising ideas
It helps to prioritize and focus efforts on the most promising product ideas. It’s easy to get overwhelmed by the number of potential ideas that come from an ideation session or design thinking workshop. The DVF framework helps you to evaluate and decide which ideas are worth pursuing.
6. Avoid wasting time on ideas that are unlikely to succeed
It helps to avoid wasting time and resources on product ideas that are not feasible or viable. The DVF framework acts as a filter that removes any ideas that are likely to fail due to known causes. It’s also a filter that protects us from our own enthusiasm and excitement about ideas. Sometimes we might love an idea but in reality it might be best to avoid it. The DVF framework helps us make this decision.
7. Creates a structured way of assessing product and service ideas
It promotes a structured and systematic approach to product development. With so many stakeholders, considerations, and ideas on the table, a structured, systematic approach to assessing ideas will keep everything moving efficiently in the right direction.
8. Encourages collaboration from the relevant experts and SMEs
It encourages collaboration and cross-functional thinking among team members. Collaboration is the key to success in design thinking and problem solving. The DVF framework encourages collaboration with a wide group of consultants and stakeholders to ensure that any assumptions are cross checked and based on expert advice.
Using the Framework to Assess Desirability, Viability and Feasibility
Identify and Analyze Desirability Factors
Desirability is how much people want the product and whether it meets their needs and desires.
When working with the DVF framework, assessing desirability is key to understanding if an idea can succeed in the market.
The desirability of a product is how much people want it and whether it meets their needs.
There are various ways to measure its impact: user research and personas provide insight into people’s needs and desires, while customer journey maps reveal their behavior; gathering feedback from industry trends can also be very valuable when gauging success potential.
Assess Feasibility in Your Environment and Target Market
Feasibility refers to whether it is technically possible to create the product.
Knowing what is achievable with your resources and time frame makes all the difference when it comes to designing a product or service.
It’s important to not only consider technology and budgets but legal and regulatory issues as well in order to truly assess feasibility before committing to any idea.
Evaluate to Ensure Viability in the Marketplace
Viability refers to whether the product is financially sustainable.
It’s important to assess viability before designing a product or service in order to determine whether the idea aligns with the budget and can be profitable in the long term.
There are several factors to consider when assessing viability, including market demand, pricing, cost of production, and revenue potential.

5 Practical Steps to Implementing the Framework
The next section will explore practical steps for implementing the DVF framework:
1. Understand your target audience and their needs/wants
Understanding the needs and wants of the target audience is essential in order to create a successful product or service.
By researching user personas, customer journey maps and industry trends, you can gain valuable insights needed to design an effective product that meets people’s expectations and fulfills their needs.
This will also help you market your product or service more effectively by targeting the right audience with the right message.
Understanding what motivates certain audiences will allow you to tailor content or features for maximum appeal.
This leads to higher customer satisfaction and better ROI for your project.
2. Brainstorm potential solutions that satisfy these needs
Brainstorming potential solutions allows us to generate many ideas and solutions in a short amount of time.
This stage is critical in order to ensure that all possible options are explored and assessed, which can lead to more creative and innovative solutions than if a single solution was pursued right away.
3. Determine which solutions are likely desirable, feasible, and viable
The DVF framework ensures that the ideas are desirable, viable, and feasible in the target market.
By evaluating ideas through this process, businesses can determine if a product or service has the potential to succeed and be profitable in the long term.
4. Test potential solutions with users
Testing ideas with customers before investing in developing a possible solution allows us to gain an understanding of how well the product will be received in the market.
Testing allows businesses to validate ideas, gather feedback, and gauge customer satisfaction. It can also provide valuable insights into people’s needs and wants, as well as any potential usability issues.
5. Develop a plan for implementing the solution
Developing a plan for implementing the solution at this stage is important because it outlines the steps that need to be taken in order to successfully launch and market the product.
It provides a framework for understanding how all of the different components of the project are connected, and how they interact with one another.
The plan should take into account both short and long term goals, as well as any potential risks or issues that could arise. This plan will help the business stay on track and ensure that no steps are forgotten or skipped in the development process.
Launch the product/service to the target marketThe final step is launching the product or service to the target market.
Key Takeaways
- IDEO’s Desirability, Viability, Feasibility (DVF) framework is a product prioritization method that evaluates three key aspects of a successful product: desirability, technological feasibility, and viability.
- The DVF framework can help the design thinker to evaluate and prioritize ideas during the innovation process and to assess which features and functionality are important to include in a minimum viable product (MVP).
- Desirability refers to how much people want the product and whether it meets their needs and desires. Feasibility refers to whether it is technically possible to create the product. Viability refers to whether the product is financially sustainable.
- The DVF framework can be used in combination with other tools and processes, such as user research and prototyping to create successful products.