Design Thinking and Six Sigma are two popular problem solving processes.
Design Thinking helps organizations identify and solve complex human problems through user research, collaboration, and creativity.
Six Sigma helps organizations optimize their operations and achieve high levels of quality and efficiency.
But which one is right for your organization?
In this article, we’ll compare Design Thinking and Six Sigma side-by-side to help you decide.
Differences Between Six Sigma and Design Thinking
Here are the characteristics of Six Sigma:
- The goal of Six Sigma is to achieve near-perfection in business processes
- It’s a quality control methodology that aims to reduce defects in a process by identifying and eliminating root causes of errors
- It uses a linear, step-by-step approach to problem solving
- It’s focused on efficiency and quality
- It’s focused on reducing variation in a process
- It’s focused on improving existing processes
- It typically uses quantitative methods
- Six Sigma projects typically use a team of specialists
- It uses data and statistical analysis to identify problems and find solutions
- A project manager typically leads six Sigma projects
- Six Sigma projects typically have well-defined goals and timelines
- Six Sigma relies heavily on process mapping and root cause analysis
- Six Sigma typically requires more resources and time than design thinking projects
Here are the characteristics of Design Thinking:
- Design thinking aims to create innovative solutions to complex human problems
- It’s a human centered design process that begins with understanding the needs of end users and then designing solutions that meet those needs
- Design thinking is focused on innovation and creativity
- It’s a fluid, flexible, and iterative process
- Design thinking focuses on creating new solutions, products and services
- It often relies on qualitative methods
- Design thinking is focused on innovation and meeting user needs
- Design thinking projects often use a diverse multidisciplinary team
- Design thinking relies on empathizing with users through observation
- A designer typically leads design thinking projects
- Design thinking projects may be more open-ended and ambiguous
- Design thinking relies on participatory design, collaboration, brainstorming, and prototyping
What Is Six Sigma
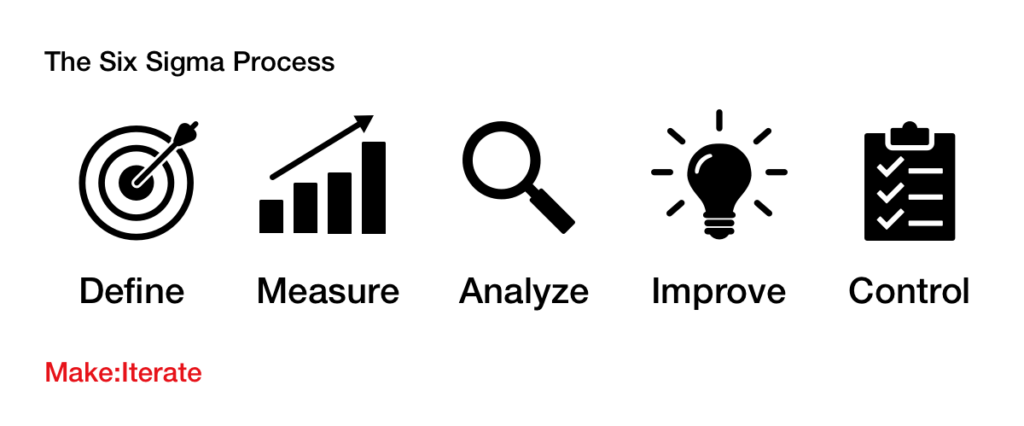
Six Sigma is an operations management methodology used by organizations to improve process performance, manage risk and streamline operations.
The principle behind Six Sigma is that all processes experience variation, which can be quantified with a statistical measure known as the sigma.
It is called ‘Six Sigma’ because organizations strive to reduce variation in operations and processes to six standard deviations from the mean.
Six Sigma was first developed at Motorola by engineer Bill Smith in the 1980s and has since been adopted by many other companies worldwide.
Today, implementing Six Sigma begins with Sigma Training so that personnel and volunteers learn how operations can be better managed and improved.
By applying two principles: Lean Startup and Process Improvement, organizations can:
- Identify areas of operations to make improvements or achieve a result.
- Eliminate waste from projects and processes.
- Provide value-added services or products faster and reduce costs.
With increased performance resulting from effective operations management inspired by Six Sigma principles, businesses can become more competitive while providing superior products and services for their customers.
When Should Six Sigma Be Used
Six Sigma is a project management technique designed to create efficient processes and reduce process defects using an iterative approach to process design.
It can be used to improve the processes for delivering products and services, making it applicable to healthcare, the service industry, construction, or any other business involved in delivering a product or service.
For example, Six Sigma processes can mitigate errors within a healthcare organization’s medical transcription services or improve the quality control of construction equipment being rented out.
Generally speaking, if a task requires efficient processes and lower error levels, then Six Sigma is very beneficial.
Despite its name implying its suitability only for the manufacturing industry, Six Sigma has proven effective in many sectors beyond the traditional factory floor.
Advantages of Six Sigma
- Six Sigma can help to reduce the amount of waste in a product or service.
- Six Sigma can help to reduce the number of defects in a product or service.
- Six Sigma can be used to improve the quality of a product or service.
- Six Sigma can help to improve customer satisfaction.
- Six Sigma can help to increase profits.
- Six Sigma can help to save time.
- Six Sigma can help to reduce the cost of production.
- Six Sigma is flexible and can be adapted to fit the needs of any organization.
Disadvantages of Six Sigma
- Six Sigma can create silos within an organization, as employees focus on meeting their individual objectives rather than working collaboratively.
- The implementation of Six Sigma may also result in the loss of some jobs as businesses streamline their operations to meet the new standards.
- Six Sigma can be time-consuming and expensive to implement.
- Six Sigma requires a great deal of employee training, which can be costly.
- Some businesses may find Six Sigma too rigid and inflexible.
- There is a risk that employees may become overloaded with work if they are expected to meet Six Sigma standards.
- There is also a risk that employees may become demotivated if they feel that the standards are unrealistic or unattainable.
- If not appropriately managed, Six Sigma can lead to a decline in quality rather than an improvement.
What Is Design Thinking
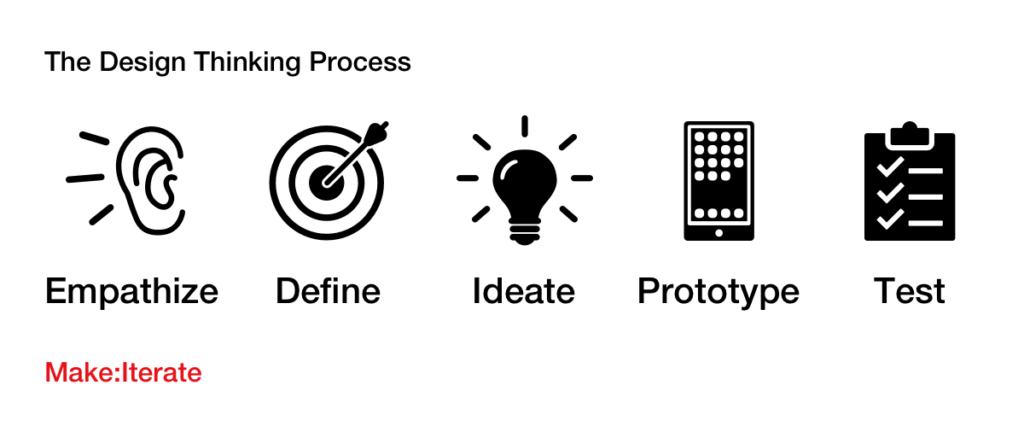
Design Thinking is a human centered design methodology focused on creating innovative solutions to complex customer-driven problems.
It originated in the design world and has been used by innovative design teams for many years. It is now used across private and public sectors as an iterative process to arrive at creative solutions to ill-defined or ‘Wicked’ problems.
Businesses can use it as a tool for creating innovative products, services, and processes where creativity and ingenuity can give the edge in an increasingly competitive market.
Design thinking starts with understanding the actual needs of customers by considering their points of view and building from there.
A design team then reviews data, generates ideas, tests those ideas, obtains feedback from customers, refines those ideas further in response to customer feedback, and eventually comes up with tangible results that address the original problem.
It’s a powerful tool for businesses in helping them tackle complex challenges quickly, efficiently, and cost-effectively by improving customer satisfaction while also reducing costs associated with the risk of not meeting customers’ needs.
Anyone can benefit from it, whether they’re a manager, designer, or entrepreneur working towards finding innovative solutions to real-world challenges.
When Should You Use Design Thinking
The Design Thinking process puts people, their behaviors, and their motivations at the center of the innovation process.
This makes it effective at solving problems that require understanding customer expectations, needs, and the customer experience with the goal of producing innovative ideas.
The Design Thinking approach can be used to build a knowledge base about the customer and explore a range of solutions before development.
It can then work alongside development to build the knowledge base and improve the product over time. This makes it an excellent complement to the agile methodology of software development.
It differs from traditional analytical problem solving – effective at solving complex technical issues – in that it strongly emphasizes empathy and collaboration, using tools and frameworks to explore an issue from different perspectives.
This method can be applied to many industries requiring new user-centered solutions, such as product design, software development, organizational development, education, or service design.
Design thinking helps foster user-centric cultures and deal with ambiguous problem areas with a focus on learning and continuous improvement.
Having an open attitude about experimentation and failure encourages learning from any mistakes made to finding successful solutions.
Overall, Design Thinking can be used in various situations where creativity is needed to find new solutions to complex human issues.
Advantages of Design Thinking
Design Thinking can help you come up with an innovative solution to a problem that is difficult to define due to humans’ complex and changing needs.
This sets Design Thinking apart from traditional analytical problem solving and makes it an effective tool for social and environmental projects and the development of new products and services.
- Design thinking can be used to tackle wicked problems, which are complex problems that do not have straightforward solutions.
- It’s an iterative process that helps to ensure that solutions are user-centered and effective.
- It can help to better understand the needs of customers or users.
- It can help to navigate ambiguous, hard-to-define problems.
- It can help to generate new ideas and think outside the box.
- It’s a flexible process that can be adapted to different contexts and situations.
- Design thinking can help reduce the risk of failure when launching a new product or service.
- It’s collaborative and brings together people with different skills and perspectives.
- Design thinking can help to build consensus and get buy-in from stakeholders.
Disadvantages of Design Thinking
The Design Thinking process can be time-consuming, challenging, and produce unpredictable results due to its reliance on continuous learning and experimentation.
This can make it more challenging to sell as a process to organizations trained in traditional business practices of linear analytical problem solving and management practices.
Because the outcome isn’t known in advance, it can be more challenging for business stakeholders to buy into it as it can be more difficult to predict earnings of any expected outcomes.
- The results of design thinking can be unpredictable
- It isn’t appropriate for complex technical issues
- It requires a lot of collaboration
- It can be challenging to get buy-in from stakeholders
- There is no guarantee of success
How to Combine Design Thinking With Six Sigma
Design Thinking and Six Sigma have traditionally been seen as two distinct approaches to problem solving, but integrating the two can lead to powerful results.
Design Thinking is a creative, out-of-the-box approach that builds on user insights and creative ideation while keeping user experience at its core.
Six Sigma aims to identify causes of failings in processes and use systematic tools and strategies to eliminate them.
Combining the two brings together a carefully structured framework with agility, enabling organizations to efficiently tackle their most complex challenges by rapidly improving problems through experimentation, optimization, and analysis.
Ultimately, by taking the best aspects of both processes for use in tandem, businesses can increase output with higher quality and reduce costs.
Conclusion
Organizations can create powerful teams equipped to solve complex customer-driven problems by integrating Design Thinking and Six Sigma methods.
Each approach has its strengths that, when combined, can create a well-rounded team of problem solvers.
What do you think about combining these two approaches? Have you tried it in your organization?