The empathy stage is a critical step in the design thinking process.
To design products and services that people love, we need to understand the world from their point of view.
User research is essential to building empathy because it provides designers with firsthand insights from users about their needs and experiences.
By conducting user research, designers can better understand their users and develop products that meet their needs.
This article will discuss empathy, how to cultivate it, and how it can help your design process.
What Is Empathy, and Why Is It Essential in Design Thinking?
Empathy is the ability of an individual to understand, share, and take on the feelings or emotions of another.
It plays a vital role in the design thinking process because it allows the designer to view problems from the users’ perspective and understand what people are experiencing to develop solutions that meet their needs.
Practicing empathy helps designers be more understanding, compassionate, and aware of the contextual elements surrounding a project, making it easier for them to craft meaningful designs that create positive experiences.
Building user empathy can help us to design user friendly products and identify new opportunities to improve the customer experience.
What Roles Does User Research Play in Helping Us Empathize With Users?
User research is essential to the empathize phase in human centered design because it provides designers with firsthand insights from users about their needs and experiences.
This helps designers understand user problems and frustrations more accurately and develop solutions more likely to meet user needs.
User research helps us to check our biases and assumptions, most of which we’re likely unaware of. Letting go of your own ideas about the experience and spending time with customers is an enlightening part of the process.
Additionally, user research can help identify patterns in user feedback that may otherwise be overlooked, providing further insights into the users needs and preferences.
How to Gain Empathy Through User Research
User research is typically conducted in three phases.
We conduct UX research before a project to understand user needs and problems.
We then speak to customers throughout a project to validate our understanding and deepen our insights, before then testing our work with customers to get feedback on how to improve our solutions.
Here’s a step-by-step process to plan and conduct your research:
1. Define Your Research Question
The first step in planning your research is to define your research question. This will help to focus your study and ensure that you are looking for information relevant to your design problem.
2. Identify Your Target Audience
The next step is to identify your target audience. This will help you determine who you need to talk to to get the information you need.
3. Choose Your Research Methods
Once you have defined your research question and identified your target audience, you need to choose the research methods you will use to gather information. Some standard research methods include interviews, surveys, focus groups, and observations.
4. Develop Your Interview or Survey Questions
If you plan on conducting interviews or surveys, you will need to develop a list of questions. These questions should be designed to elicit information about your target audience’s needs, wants, and experiences.
5. Choose Your Observation Locations
If you plan on conducting observations, you will need to choose locations where you can observe your target audience in their natural environment. This could be a place of work, home, or leisure.
6. Choose a Date and Time for Your Research
Once you have chosen your research methods and developed your questions, you must select a date and time. Choosing when your target audience is likely available and willing to participate in your study is essential.
7. Recruit Participants for Your Research
If you are conducting interviews or focus groups, you will need to recruit participants for your study. You can do this by reaching out to individuals or organizations that represent your target audience.
8. Conduct Your Research
Once you have recruited participants and chosen a date and time for your research, it is time to conduct the investigation. This involves carrying out the preferred research methods and collecting the data that has been gathered.
9. Analyzing the Data
Once the data has been collected, it will need to be analyzed to extract meaning from it. This can be done through various methods, such as statistical or qualitative analysis. The data analysis stage is where you will begin to answer the research questions you defined at the beginning of the process.
10. Reporting the Results
After analyzing the data, you will need to report the results of your research. This can be done through a written report, an infographic, or a presentation. It is essential to communicate your results clearly and concisely to provide valuable insights to your client or team
How to Choose a Research Method for User Research?
Choosing the proper research method for the task is essential when conducting user research.
A thorough research study will contain a mix of qualitative and quantitative research methods. This helps to get a well-rounded view of the customer and their experience.
Ultimately it comes down to what research question you have and what you need to learn.
Some standard research methods include interviews, surveys, focus groups, and observations.
Interviews are a great way to gather qualitative information about users’ needs, motivations, and behaviors. They allow you to ask questions and get feedback directly from users.
Surveys are an excellent way to gather quantitative data on a large scale. They can collect information about users’ preferences, behaviors, and expectations.
Focus groups are an excellent way to get feedback from multiple users at once. This allows you to gain insights from various people and benefit from hearing their discussions and reflections.
Observations are a great way to see how users interact with your product or service in their natural environment. This can help you identify usability issues and understand how users use your product.
A combination of the techniques above can help to build a knowledge base to support design decisions throughout the project. Choose the ones that meet your needs and experiment with different techniques to find the combinations that work for your specific needs.
8 Methods for Understanding User Needs
Let’s get a deeper understanding of the research methods to help you understand which ones would work best for your project.
1. Surveys
Surveys can be administered in person, by mail, or online. They typically consist of questions that respondents answer to provide information about their needs and preferences.
2. Focus Groups
Focus groups are groups of people brought together to discuss a particular topic. The discussion is typically led by a moderator asking questions and probing for deeper insights.
3. Interviews
A user interview involves a conversation between a researcher and a respondent in which the researcher asks questions and the respondent provides answers. Interviews are typically conducted in person or on a video call.
4. Observation
Observation is another common research method for understanding user needs. It involves observing people as they go about their everyday lives and noting their behaviors and interactions with their surroundings.
5. Usability Testing
Usability testing helps us to understand if the product we’ve designed is usable and how we can improve it to make it more user friendly. It involves having users interact with a product or service to assess its usability and effectiveness. User testing can be conducted in person or online.
6. Heuristic Evaluation
A heuristic evaluation involves having experts assess a product or service against a set of usability guidelines to identify potential problems and areas for improvement.
7. Contextual Inquiry
A contextual inquiry involves conducting interviews with users in their natural environment to observe them using the product or service in context.
What’s Next? Creating Useful UX Artifacts
Once you’ve gathered information about users’ needs and preferences, you’ll need to create artifacts that make that valuable data throughout the rest of the project.
Here are 4 common UX design artifacts to help you share your findings:
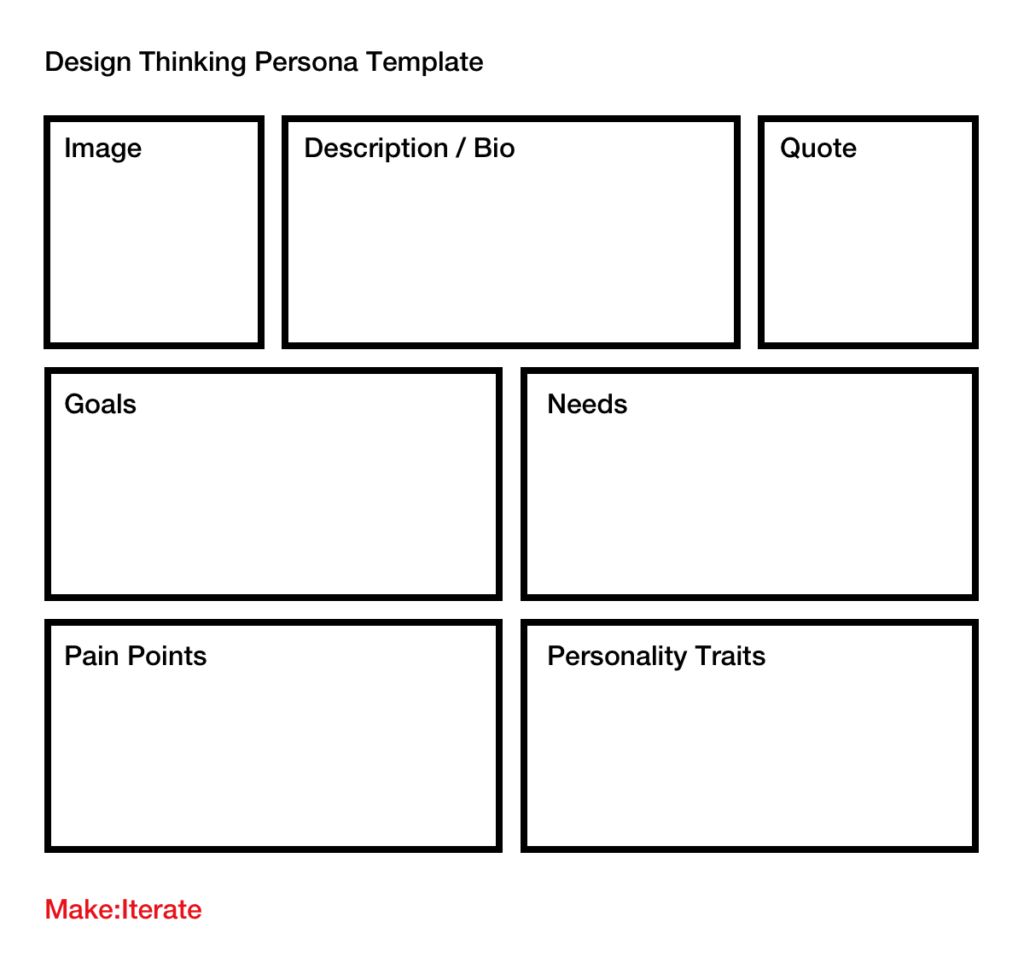
User Persona
Knowing your target customer can go a long way in helping you reach them the most effectively. A way to accomplish this is creating a user persona, a profile of your ideal customer that you reference when making decisions about how to design, market or sell your product or services.
Providing a detailed picture of who the end users are will enable the design team to tailor their approach based on the customers’ needs, wants, and actions; it also encourages consistent decision making across the lifecycle of software development.
Creating a user persona involves collecting data about your ideal customers and then using that data to create an in-depth profile outlining the commonalities of who utilizes your products or services.
It may include demographics such as age, gender, and job title; psychographics such as values and attitudes; interests and lifestyle behaviors; and what tools they use and where they search for information.

Customer Journey Map
A customer journey map is a tool to visualize the entire customer experience with a product or service. It tracks the customers’ steps throughout their journey, from when they first become aware of the product to their post-purchase behavior.
The importance of creating a customer journey map comes from its ability to identify areas for improvement in the customer experience and develop strategies accordingly.
Creating a successful customer journey map involves using data gathered from user research, surveys, website analytics, and other sources that follow interaction points with customers.
Analyzing this data helps to uncover critical insights often not found in conventional analyses. By considering everything a customer experiences throughout their customer journey, teams can solve problems and remove friction at each step in the journey and improve the overall user experience.

Empathy Map
Empathy mapping is a powerful way to gain insight into the customers’ world. It is a collaborative process that helps teams understand their customer from different angles by questioning what their customers think, feel, hear, see and say.
Using the data gathered from user research, combined with our user personas, we map insights into categories that help us get a well rounded view of our customers’ experience.

UX Storyboards
A UX Storyboard is a visual representation of the user experience for an environment, product, or process. It is often used to design, visualize and communicate ideas during the product design process.
UX Storyboards are essential to successful product design because they outline the flow of how the end user engages with your product in the real world.
In addition to providing valuable insight into the user’s journey using the product, they also help create a shared mental model of this direction amongst all involved teams.
Creating a UX Storyboard can be done by first establishing a sequence of significant steps and minor tasks that will be part of each step, then adding images or relevant content to bring these steps to life.
All storyboard panels should provide enough detail to ensure users know what will happen throughout their journey with your product.
By creating an effective UX Storyboard, teams can align on who they’re designing for, what specific problems they’ll solve, and what a successful outcome looks like, before heading into full production mode.
Conclusion
Designing with empathy is essential to creating products that appeal to users. User research helps us gain the understanding we need to design an innovative solution that meet user needs in the best possible way.
By conducting UX research before, during, and after a project, we can validate our understanding of users and ensure that we are designing products that they will love.